 Visit Elective Africa website Visit Elective Africa website
|


|
|
|
| Elective Africa Monthly Newsletter |
|
Meet Elective Africa near you and find out more about our educational and expedition travel opportunities to Africa. This September we will be visiting schools in Washington DC, Virginia, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, New York, Atlanta, Dallas, Houston, Seattle and Boston. We would be happy to have you join us if you will be within our locations of visit as we reach out to more students on our Pre-health and Healthcare programs. The idea of our school visits is so that we can meet with advisors, students and clubs officials to listen to your needs and what you are seeking so that we can be able to deliver an exceptional experience to you. In this issue, Meet Medical Students from Medical University of Bialystok University, Poland who carried out their medical elective at Mt. Meru Regional Hospital in Arusha, Tanzania. Find out what they had to say. Back to top |
| Social Cultural and Political Context of the Kenyan Health System |
 |
|
Top in the Radar of determinants of health and wellbeing in any country is the social- cultural and political factors. In trying to understand the Kenyan health system it is key to thus dissect some specifics that play into influencing its progress. Strong cultural norms and values that influence behavior These norms affect the health seeking behaviors, intake of preventive measures as well as the value attached to health education. The norms thus result into the rise of lifestyle diseases and the ease of spread of communicable diseases. The often common reliance on traditional medicine including the local herbs which are not scientifically approved results into brooding of illness and the consequential presentation of cases at a very advanced stage of infection. Advanced cases require specialized skills and equipment to manage thus a major strain on the health system. Poorly operationalized social dimensions of health The social dimensions include the availability of the resources for the populations to meet the daily needs that is poverty which results in the low health status among the populations. Accessibility of the health system is another social dimension which results in a challenge while the system wants to maximize on its reachability by the people there is also the element of there being little accessibility as well as the system not being able to achieve the health services when and where needed. The road systems connecting the populations to the health system is poor and thus people are hesitant to visit the health system or at times unable to. New challenges to health and the health systems The rise in the non-communicable diseases and the frequent up rise of the communicable ailments results into a strain into the resources that are at the disposal of the health system. The rise in road transport Accidents is a major contributor to the strain in the health system. The health system has to frequently adapt to changing circumstances and with the constrain of resources both human and capital this is often a slow process. With rise in technology there is a need for new equipment and set of skills among the healthcare providers the health system has to therefore Rising expectation and the growing dissatisfaction With rise in globalization and technology the health system is faced with the reality of a more informed patient. As the patient is seeking the service they have a rough idea of what should be given to them and in what proportion including knowledge including the right to information. The doctors and the health system have to respond to particular patient requests and in the absence of that there is a rise in dissatisfaction which reduces the faith that the patient populations have on the public health system. Poor stewardship Part of the other social factor is the absence of top quality stewardship of the health system which results into a corrupt system and non-priority resource allocation to healthcare needs, this leads to failure of the health system to live by standard and to orient itself to the current needs of the populations hence poor service delivery. Back to top |
| Understanding the Drug Resistance Menace |
 |
|
Fact File In 2012, WHO reported a gradual increase in resistance to HIV drugs, albeit not reaching critical levels. Since then, further increases in resistance to first-line treatment drugs were reported, which might require using more expensive drugs in the near future.\ In 2013, there were about 480 000 new cases of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB). Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) has been identified in 100 countries. MDR-TB requires treatment courses that are much longer and less effective than those for non-resistant TB. In parts of the Greater Mekong sub region, resistance to the best available treatment for falciparum malaria, artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs), has been detected. Spread or emergence of multidrug resistance, including resistance to ACTs, in other regions could jeopardize important recent gains in control of the disease. There are high proportions of antibiotic resistance in bacteria that cause common infections (e.g. urinary tract infections, pneumonia, bloodstream infections) in all regions of the world. A high percentage of hospital-acquired infections are caused by highly resistant bacteria such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA) or multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Main causes of drug resistance in developing world With the menace of antimicrobial resistance continuing to sail across the global health system, this month we set our eyes into understanding some of the sector specific causes of drug resistance in sub Saharan Africa.
Selection of resistant microorganisms is exacerbated by inappropriate use of antimicrobials. Sometimes healthcare providers will prescribe antimicrobials inappropriately, wishing to placate an insistent patient who has a viral infection or an as-yet undiagnosed condition. This may be prompted by the heavy patient load that awaits the providers on day to day basis. Poor prescription is a major contributor to the menace of drug resistance.
In our previous editorial focuses we have mentioned the absence of resources as a unique factor in our health system. The absence of diagnostic equipment including the lack of service of the existing equipment results in errors in telling out what the patient is suffering from. Assumed and erroneous prescriptions have their trace here and in general perspective it results in drug resistant.
In Africa and to say Kenya and Tanzania for example the regulations on counter purchase of drugs are absent. The patients thus use their symptoms to seek for drugs and without proper prescriptions they use them. This is a major factor fueling the spread of drug resistance since there is little follow up on proper adherence to prescription as well as the chance of error in using symptoms to guess one’s illness.
Critically ill patients are more susceptible to infections and, thus, often require the aid of antimicrobials. However, the heavier use of antimicrobials in these patients can worsen the problem by selecting for antimicrobial-resistant microorganisms. The extensive use of antimicrobials and close contact among sick patients creates a fertile environment for the spread of antimicrobial-resistant germs. Besides the lack of proper infection control measures within the hospital set up leads to the spread of this infections. There is thus need to adopt preventive measures and have proper guideline to the use of the drugs and infection control.
This is a factor that speaks to the research arm of the healt6h system calling on it and the need to continually develop alternative solutions treatment plans and options for the various illnesses. This is key to ensuring that in the event of a noted resistance there is a tested alternative. Absence of alternative is a major cause of the resulting morbidity and mortality from drug resistance cases. It’s a global threat, requiring a global solution but it is much more about the action taken by the local health system to address the sector specific and controllable valuables in drug resistance. Back to top |
| The EA Medical Elective Experience |
 |
|
Medical Students from Medical University of Bialystok - Poland Placement Destination: Arusha, Tanzania Hospital Placement: Mt. Meru Regional Hospital Elective Africa understands the specific needs of healthcare service providers at every level of experience and design placements that offer focused and well-rounded elective opportunities to medical elective students. Our aim is to help you grow as a healthcare service professional. We offer you a life-changing opportunity to experience medicine in a manner every healthcare professional who wishes to make a difference needs to. Back to top |
| From Door to Door in Fight for Malaria in Migori County |
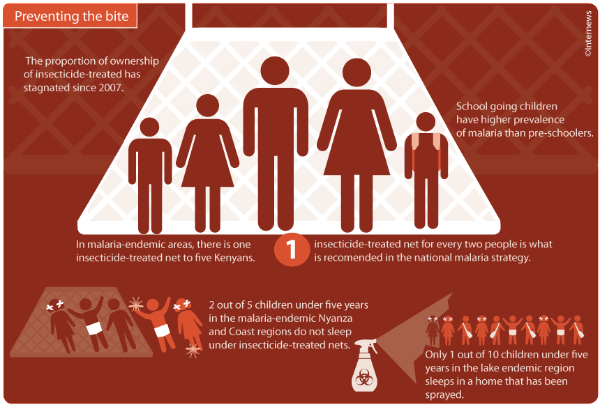 |
|
“Controlling malaria does more than improve human health. It boosts social well-being and economic development. I urge the global health community, including political leaders in endemic countries, to maintain their commitment to provide universal access to malaria interventions and end needless suffering from this preventable and treatable disease.” The UN Secretary General Ban Ki-moon Malaria is one of the biggest killer disease in Kenya; with a percentage of 3, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. WHO indicates that deaths caused by malaria are more pronounced in children under the age of five. In a bid to control the disease, the Ministry of Health Migori County has trickled down national malaria interventions to the village level through the successful implementation of the Global Fund Malaria. The aim of funding is to ensure that at least 80 percent of people living in malaria prone counties are equipped with knowledge on prevention and treatment of malaria. The global funds need to make significant progress with the funding cycle of 2014 – 2016 before the next funding in 2017 – 2019. The progress can be achieved by strengthening advocacy, communication and social mobilization capacities for malaria control. Increasing community member’s knowledge on prevention and treatment of malaria involves utilizing various techniques to get the message across and to get people aware and responsive to the ongoing threat of malaria in the high risk areas. The greatest source of information on malaria for community members is gathered from the Community Health Workers (CHWs), hence it is vital that they acquire relevant and up to date information on diagnosis, prevention and treatment of the disease. The county with the help of volunteers oversaw the training of 120 CHWs on Community Health Strategies and another 240 on Malaria Case Management. The ministry of Public Health uses various means to promote education including; facilitating supervision of peer-to-peer on job mentorship by arranging exchange visits between newly formed Community Health Teams with those who are more established. The Health Management teams also supports the capacity development of the CHWs.Community dialogues and field days are conducted to engage the residents in barazas (forums) where they discuss malaria related issues. These discussions are guided by the indicators outlined in the Ministry of Health tool, also known as the “chalkboard” (Kenya NGO’s Alliance Against Malaria) KeNAAM supports 17 community health units to organize these events, where the discussions were facilitated by the CHWs, who ensured that focus is maintained on malaria. The community members brainstormed on the problematic areas in addressing malaria and proposed workable solutions to deal with the identified challenges.
During the subsequent Health and Action Days, the communities would review the previous problems raised and assess how well the measures they had proposed worked in order to inform future strategies. In collaboration with the communities and different stakeholder in Migori County, medical camps were organized where a total of 875 community members were tested for HIV and malaria. The Community Health Workers demonstrated to the participants how easy it is to be tested for these conditions and they introduced the rapid testing for malaria which has increased the locals’ acceptance of this tool during household visits. Never dealt with malaria before? Come experience first-hand! Book Now Back to top |
|
|

 9 2016
9 2016