 Visit Elective Africa website Visit Elective Africa website
|


|
|
|
| Elective Africa Monthly Newsletter |
|
Things just got better! This fall we will be on a US Road Show. Like you, we also get to travel. If you are in the US, LET US KNOW which State, we got something for you. This summer, it has been our joy to place students for electives and pre-health shadowing in Nairobi, Mombasa, Malindi and Arusha. Currently we have students from Bialystok University, Queen's University Belfast, Trinity Western University and University College Dublin. In this issue, Sari Cooper from Georgetown University shares her pre-medical reflection with us. You got to read it. Back to top |
| What Makes an Ideal Health Care Practitioner |
 |
|
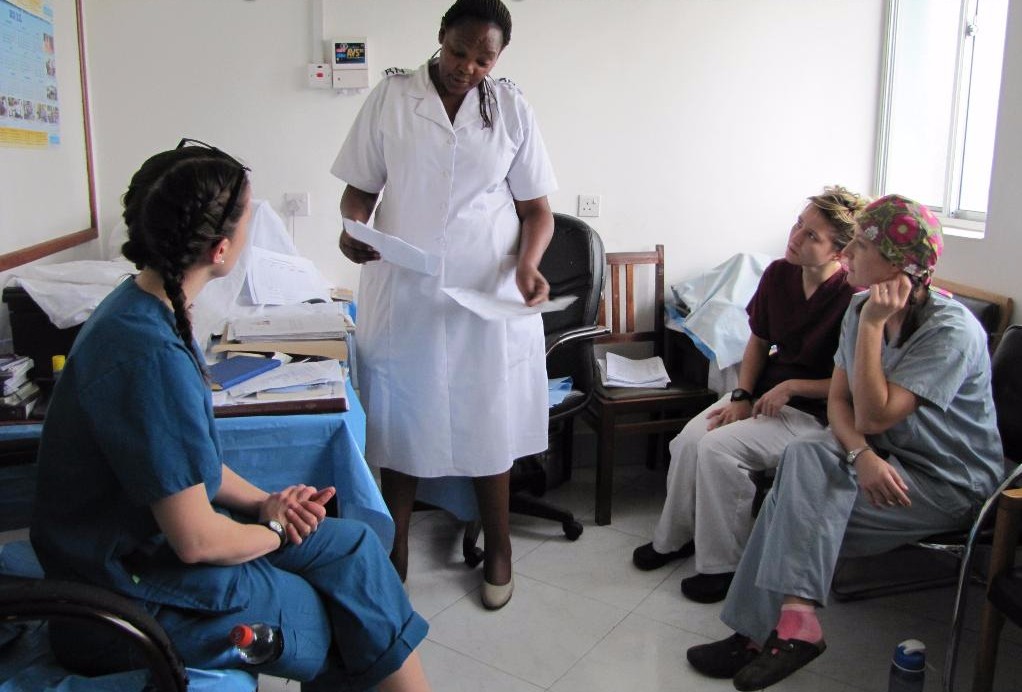
Any form of healthcare training is endowed with a series of extensive and broad theoretical training. This arises because of nature of the healthcare profession which more often than not involves matters of life and death. Similarly, a career in the healthcare field can be very taxing and thus to endure the tides and waves and stand out to deliver complete and comprehensive care to the patients one needs more than the skills acquired in the lecture hall or the simulations laboratory. The Accredited Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) provides a guideline on some of the competencies essential on evaluating the outcome of residency training, this include patient care; medical knowledge; practice-based learning and improvement; interpersonal and communication skills; professionalism; and systems-based practice In trying to interpret the framework and relate it to the broad healthcare training some of the essential skills that one requires are: Empathy – It is often said that for you to deliver care you must learn to first see the person before you see the patient. Understanding and being able to empathize and/or sympathize with the difficult situations faced by others is key to delivery of compassionate healthcare. This skill enables one to assume the position of the person they are dealing with at all time and thus do their best to ensure that they deliver appropriate and effective care for the promotion of health. Communication Skills – Across the board all writers of patient provider articles have placed communication at the epitome of healthcare delivery and most importantly at the heart of patient provider relationships. To understand the patient one has to engage them this is only made possible by communication. The skill of listening keenly, attention to detail and proper feedback giving is part of what the communication in this field needs so much. Be a Team Player – While the roles in the healthcare delivery for the various professionals is clearly defined, there are linked together to ensure wholesomeness of the service. To excel in the healthcare field one needs learning how to succeed within a team context. Joining group studies while at school, joining associations and clubs is another sure way of building once ability to succeed within the team context. Dealing with Pressure – Pressure is a daily part of many healthcare cadres, a rude and uncooperative patient, a colleague who blames you for an act you even have no idea of, watching a patient die are part of the highlights that the professionals have to endure on daily basis. As one seeks to excel within the healthcare field they should learn how to be able to handle it, and thrive on it. In developing world, the pressure is even accelerated by the absence of enough resources and the large number of patients. Skills in handling pressure can be developed through an interaction with those who have thrived in such an atmosphere. Strong Work Ethic – Ethics are a core domain of this profession. Starting with regulations on what one ought to do across to how they are supposed to do it. Healthcare professionals have to be fully aware of the guidelines that regulate their behavior and guide their conduct. Learning how to apply the principles of confidentiality, autonomy, justice and beneficence in the health system is key to ensuring success within the field. This is a skill one cannot miss in this profession. Positive Mental Attitude – There will be difficult days ahead; many cases that will lower your morale, disappointing situations when you did your best but the situation didn’t get better. The key to excellence here is to ensure that you carry along with you a very positive mental attitude that it’s going to be better and that the single case that has gone in the wrong direction is a milestone to many glories ahead. While these outlined skills are paramount they narrow down to one thing self-confidence. Being a confident provider makes the care you deliver have the element of accuracy and also helps in building these skills. The key question is where are these skills learnt? Is there a special school for it? What does one need to do in order to develop them? During your elective term or your shadowing experience you should contemplate going into health systems that have unique attributes often different from your home areas. With Elective Africa you make the biggest stride in developing these skills as you also grow your clinical competence. Back to top |
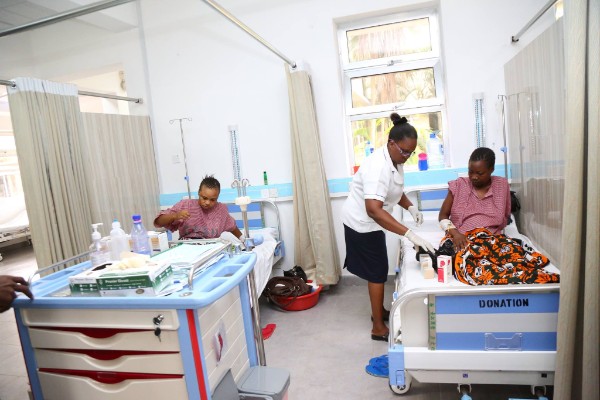
| How Safety is Maintained within the Hospital Set-Up - Kenya |
 |
|
The healthcare personnel and patients operate in an atmosphere that has a big potential for infection. As one seeks to understand the completeness of healthcare delivery an aspect that continually crops is just how do hospitals in the developing world arm themselves to deliver much needed care. The question is just how do the hospitals ensure that care is delivered and ensure the providers and patients are safe as they deliver the care. Fact file Coast Provincial General Hospital(CPGH) produces 60- 80 kg of waste in a day of which 20% is infectious. Each patient in CPGH produces 0.2kg of waste of which 20% is infectious. The health system has put in place some stringent measures to ensure prevention and control of cross infection within the hospital set up. Some of the measures include: Guidelines on waste disposal Changes in infection control and advances in technology have resulted in the increased use of disposable clinical products which have in turn increased waste treatment/disposal volumes. Left lying around, this waste provides a breeding ground for infections and diseases which poses a serious threat to those who come across it. Some of the measures put in place to ensure proper waste disposal include: Ensuring the proper handling of the waste mainly done through the provision of clearly labelled dustbin. In the Kenyan health system, you will often and are likely to see a Red bin which is used to store the radioactive material and highly infectious material, a yellow box which is used to store sharps awaiting disposal and a black bin that is clearly labelled and used for the storage of normal hospital waste. This segregation of waste at the hospital level is key to ensuring that any potential infections arising are controlled well in advance. Ensuring the Availability of Hand washing facility within the hospital as well as clean drinking water It is estimated that washing hands with soap and water could reduce diarrheal disease-associated deaths by up to 50% Researchers in London estimate that if everyone routinely washed their hands, a million deaths a year could be prevented A large percentage of food borne disease outbreaks are spread by contaminated hands. Appropriate hand washing practices can reduce the risk of food borne illness and other infections. Therefore, an ideal hospital environment should have well labelled zones for hand washing and people should be sensitized on hand washing to ensure that resulting infections are controlled this is a core way that safety is ensured within the hospital set up.
Ensuring proper adherence to personal protective equipment This item mainly narrows to the healthcare provides, who are highly encouraged to use the personal protective equipment. This personal protective equipment ranges from the gloves to the masks and googles are used across the various healthcare delivery cadres to ensure that they are guarded from injuries and infections. The rational use of PPEs is a cardinal way of ensuring protection from preventable exposure within the health system and provision of this is a measure put in place by the health system to ensure that safety of the providers.
Continuous Education to the staff on the need for maintaining a safe environment On a regular basis the staff at the hospitals are taken through sessions that are ment to ensure that they are conversant with the expectations that are there regarding the safety and health as well as the prevention of injury and cross infection within the hospital environment. Every healthcare professional irrespective of the location comes into contact with waste that is disposed at the various levels of healthcare delivery learning how to manage it and the best practices in ensuring a safe environment.
Proper adherence to the post exposure prophylaxis One of the major concern of students especially those looking for hands on experience in areas where they may need to use sharps is the danger of needle pricks. The hospitals have clearly laid out procedures on exposure to needle or sharp pricks. The World Health Organization (WHO) says that when PEP is started immediately after exposure and the full dose completed, it can reduce the risk of HIV infection by more 80 per cent. In the operations of the hospital at levels where sharps and injectables are used there are laid down procedures to preventing infection in the event of a needle prick. The baseline in this measure of safety is report it as soon as possible.
Establishment of the health and safety committee within the hospital The hospitals within Kenya have a special unit established to ensure that the status of the health and safety is maintained at standard levels. This committee is charged with the responsibility of enforcing the above discussed. As you contemplate of travelling abroad to experience a different health system it is thus important to be aware of the various safety measure that are put in place to ensure that as one rotates in the various departments you have proper information as to how to keep your safety and that of patients. Back to top |
| My Pre-Medical Reflection - Sari Cooper |
 |
|
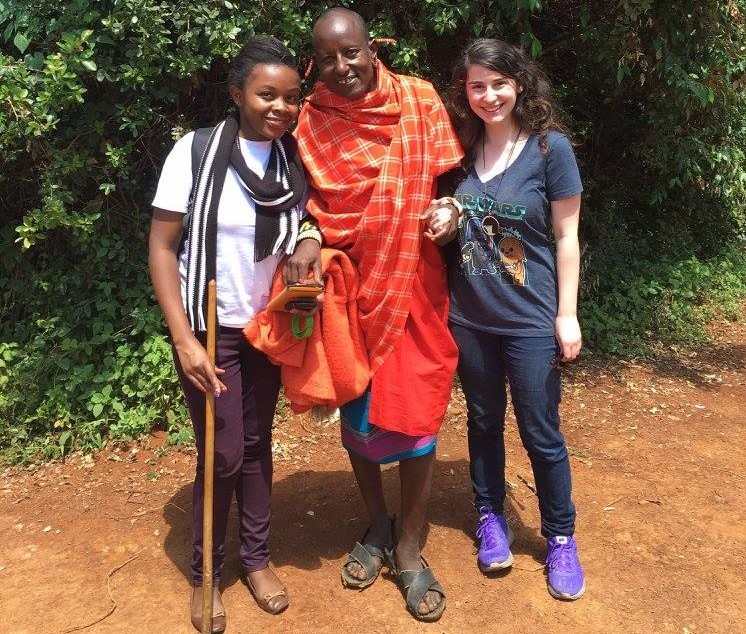
As a pre-med, I was in search of an international program through which to expand my scope of the world and gain unique experiences in the field of medicine. Luckily for me, I found Elective Africa. Despite never having traveled so extensively in my life, I found Elective Africa to be a welcoming and friendly program that instantly put me at ease. Rotations with Dr. Nikita Raval at Mbagathi District Hospital allowed me to experience the full extent of hospital life, which was truly thrilling as before now my experiences with medicine had been purely academic instead of clinical. My first week was spent in Internal Medicine. As a future Neurologist, I was extremely interested in a few neurology-related cases that came through the door, as well as a wide variety of other cases. There, I also got the opportunity to learn how to fix an IV line. I spent the next week in the Maternity ward, allowing me to connect with patients during this important time in their lives while also learning about maternal and fetal care in a foreign country. Observing a C-section was an amazing opportunity for me that I never would have experienced at this stage in my education back home. While a C-section was the epitome of the mundane for the doctors there, for me it was an eye opening journey into the world of surgeons and OBGYN’s. It was also fascinating seeing the amount of creativity involved in how a hospital with minimal resources works to secure the best patient care possible. Of course, participating in Elective Africa wasn’t just an exciting journey for me as a pre medical student, but also because I was able to travel and see sights entirely unique to Kenya. The Maasai market was an extremely unique experience and I’m so glad I got to go. I was able to get traditional souvenirs for all my friends and family. As an animal lover, the Giraffe Manor and Elephant Orphanage were also highlights of the trip. I was able to feed giraffes and pet baby elephants, a once-in-a-lifetime experience. However, my favorite part of my trip would have to be the 3-day Maasai Mara safari. It had been a lifelong dream of mine to go on safari, and having that fulfilled is something I will never forget. Finally, I have to give a shout out to Christabel Njeru and Richard Kariuki for taking me around Nairobi, teaching me some Swahili (asante sana), and for being genuinely awesome company and individuals. Also thank you to Caren and everyone else at Elective Africa for allowing me such an incredible opportunity to travel across the world to learn and live . Sari is a Pre-Med Student at Georgetown University Back to top |
| Start Planning Your Placement |
 |
|
Deciding on which part of the world to take your elective can be overwhelming. However, when you know the regions you would like to pay a visit, then it will be easier to select a particular country and what you would like to do. For instance, your interest may be on Developing countries but this is so broad. So to narrow it down, you can settle on Africa. Africa is big and it may therefore be impossible to visit the continent in 4 weeks or 6 weeks that you have planned your visit. You will now think of either East Africa, West Africa, South Africa, Central Africa or Northern Africa. Every country has its own unique attributes. Popularity of the area will therefore be dependent on your experience as a traveler and what you would like to achieve for your Health Care Placement. One fact though, Africa can be challenging but at the same time it can provide you with a rewarding health care placement destination.
From your choice of destination, you can now take care of your essentials. I am sure you did not settle for an elective in Africa because you cannot go to Asia. You decided to choose your destination because it is a dream that you want to make into a reality. You will be required to produce an introduction letter to the hospital administration of your choice. This can be inform of a signed letter by your dean, registrar or head of department. This should be done prior to your visit. After your approval by the hospital you want to contact your physician for definitive and professional advice on vaccines. For instance, if you are travelling to Africa you will be required to get a yellow fever vaccine. It is also critical that you take Malaria prophylaxis for all locations, Typhoid and Hepatitis A vaccinations are also recommended. At least 6 weeks before your departure you should have reserved your flights and accommodation. Online option will work. We often recommend our clients to get a visa at the airport on arrival, it is convenient and one less thing to worry about before your flight! Always pick the tourist visa option; it is the cheapest. For your cover may also want to get a travel insurance and a travel kit. Time is one commodity that you don’t want to lose. Get in touch and book your trip. Planning for a placement can be very exhausting. That is the extra price you have to pay to work abroad. The above guideline will be of great help. But you don’t have to go through this hustle of figuring out a new environment and culture on your own. This is where we come in. Just tell us what you need and we will make it happen. With 15 years of experience, we will be more than excited to make your elective experience in Africa worth talking about to friends. Talk to Our Team Back to top |
|
|

 8 2016
8 2016